💡 Think and Discuss!
A rectangular carpet has dimensions \((\sqrt{5} + 1)\) m and \((\sqrt{5} - 1)\) m. A square carpet has a side length of \(\sqrt{5}\) m.
Which carpet has a larger area? Which has a larger perimeter? Discuss.

📚 Learn!
Before studying how to perform arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on real numbers, we will first learn about the concept of similar radicals.
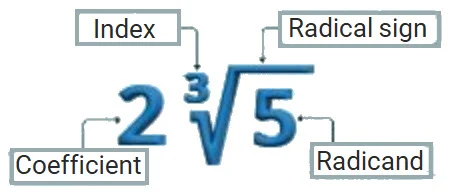
Similar Radicals
Similar radicals are radicals that have the same index and radicand.
Examples of Similar Radicals:
\(2\sqrt{3}\) and \(3\sqrt{3}\)
\(-5\sqrt{7}\) and \(\sqrt{7}\)
\(4\sqrt[3]{2}\) and \(-2\sqrt[3]{2}\)
Examples of Non-Similar Radicals:
\(4\sqrt{3}\) and \(2\sqrt{5}\)
\(\sqrt[3]{5}\) and \(\sqrt{5}\)
\(2\sqrt{7}\) and \(3\sqrt[4]{7}\)
🔢 Example 1
Given: \(x = -4\sqrt{3}\), \(y = \sqrt{3}\), \(z = \sqrt[3]{5}\). Find the value of each of the following:
Solution:
1. Solution for \(x + y\):
\(x + y = -4\sqrt{3} + \sqrt{3}\)
\(= (-4 + 1)\sqrt{3}\)
\(= -3\sqrt{3}\)
2. Solution for \(x \times y\):
\(x \times y = -4\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}\)
\(= -4 \times 3\)
\(= -12\)
3. Solution for \(\frac{x}{2y}\):
\(\frac{x}{2y} = \frac{-4\sqrt{3}}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
\( = \frac{-4}{2}\)
\(= -2\)
4. Solution for \(2x - z^3\):
\(2x - z^3 = 2(-4\sqrt{3}) - (\sqrt[3]{5})^3\)
\(= -8\sqrt{3} - 5\)
📌 Note!
- If \(x \ge 0\), then: \(\sqrt{x} \times \sqrt{x} = (\sqrt{x})^2 = x\)
- If \(x \in \mathbb{R}\), then: \(\sqrt[3]{x} \times \sqrt[3]{x} \times \sqrt[3]{x} = (\sqrt[3]{x})^3 = x\)
🧮 Example 2
Write each of the following in simplest form so the denominator is an integer:
1️⃣ \(\frac{7}{\sqrt{3}}\)
2️⃣ \(\frac{-15}{\sqrt{5}}\)
3️⃣ \(\frac{12}{5\sqrt{2}}\)
Solution:
1. \(\frac{7}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\( = \frac{7}{\sqrt{3}} \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\( = \frac{7\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
2. \(\frac{-15}{\sqrt{5}}\)
\( = \frac{-15}{\sqrt{5}}\times\frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{5}}\)
\( = \frac{-15\sqrt{5}}{5}\)
\( = -3\sqrt{5}\)
3. \(\frac{12}{5\sqrt{2}}\)
\( = \frac{12}{5\sqrt{2}}\times\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\( = \frac{12\sqrt{2}}{10}\)
\( = \frac{6\sqrt{2}}{5}\)
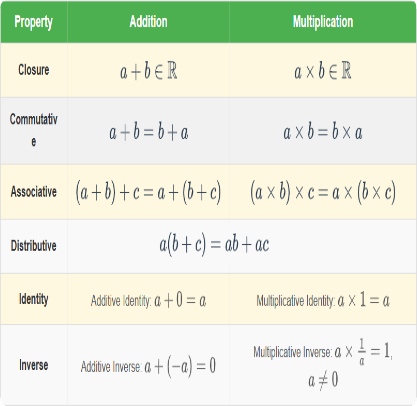
⚖️ Properties of Operations on Real Numbers
💡 Example 3
Find the result in simplest form:
1️⃣ \(2\sqrt{3}(4+\sqrt{3})-4\sqrt{3}\)
2️⃣ \((\sqrt{7}-1)(2\sqrt{7}+3)\)
3️⃣ \((2\sqrt{2}+1)(2\sqrt{2}-1)\)
4️⃣ \((2\sqrt{5}-5)^2\)
Solution:
1. \(2\sqrt{3}(4+\sqrt{3})-4\sqrt{3}\)
\(= 2\sqrt{3} \times 4 + 2\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3} - 4\sqrt{3}\)
\(= 8\sqrt{3} + 2 \times 3 - 4\sqrt{3}\)
\(= 8\sqrt{3} + 6 - 4\sqrt{3}\)
\(= 4\sqrt{3} + 6\)
2. \((\sqrt{7}-1)(2\sqrt{7}+3)\)
\(= \sqrt{7} \times 2\sqrt{7} + \sqrt{7} \times 3 - 1 \times 2\sqrt{7} - 1 \times 3\)
\(= 14 + 3\sqrt{7} - 2\sqrt{7} - 3\)
\(= (14 - 3) + (3\sqrt{7} - 2\sqrt{7})\)
\(= 11 + \sqrt{7}\)
3. \((2\sqrt{2}+1)(2\sqrt{2}-1)\)
\(= (2\sqrt{2})^2 - (1)^2\)
\(= 8 - 1\)
\(= 7\)
4. \((2\sqrt{5}-5)^2\)
\(= (2\sqrt{5})^2 - 2 \times 2\sqrt{5} \times 5 + 5^2\)
\(= 20 - 20\sqrt{5} + 25\)
\(= 45 - 20\sqrt{5}\)
✅ Think and Discuss Activity Answer
Question:
Rectangle area with dimensions: \((\sqrt{5} + 1)\) m × \((\sqrt{5} - 1)\) m
Square area with side: \(\sqrt{5}\) m
Which carpet has a larger area? Which has a larger perimeter? Discuss.
Solution:
1. Calculate Area and Perimeter for the Rectangle Carpet:
Dimensions: Length \(L = \sqrt{5} + 1\), Width \(W = \sqrt{5} - 1\).
Area \(A_R = L \times W\)
\(= (\sqrt{5} + 1)(\sqrt{5} - 1)\)
\(= (\sqrt{5})^2 - (1)^2\)
\(= 5 - 1 = 4\) m²
Perimeter \(P_R = 2(L + W)\)
\(= 2\bigl((\sqrt{5} + 1) + (\sqrt{5} - 1)\bigr)\)
\(= 2(2\sqrt{5})\)
\(= 4\sqrt{5}\) m
2. Calculate Area and Perimeter for the Square Carpet:
Side \(s = \sqrt{5}\).
Area \(A_S = s^2\)
\(= (\sqrt{5})^2 = 5\) m²
Perimeter \(P_S = 4 \times s = 4\sqrt{5}\) m
3. Comparison:
- Areas: The square carpet has a larger area since \(5 > 4\).
- Perimeters: Both carpets have the same perimeter.
🔄 Example 4
Find the additive inverse and the multiplicative inverse in simplest form for each of the following:
1️⃣ \(3\sqrt{2}\)
2️⃣ \(2 - \sqrt{3}\)
Solution:
1. For \(3\sqrt{2}\):
Additive Inverse = \(-3\sqrt{2}\)
Multiplicative Inverse = \(\frac{1}{3\sqrt{2}}\)
To simplify:
\(\frac{1}{3\sqrt{2}} = \frac{1}{3\sqrt{2}} \times \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(= \frac{\sqrt{2}}{3 \times 2} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{6}\)
Thus, the multiplicative inverse in simplest form = \(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{6}\)
2. For \(2 - \sqrt{3}\):
Additive Inverse = \(-(2 - \sqrt{3}) = -2 + \sqrt{3}\)
Multiplicative Inverse = \(\frac{1}{2 - \sqrt{3}}\)
To simplify:
\(\frac{1}{2 - \sqrt{3}} = \frac{1}{2 - \sqrt{3}} \times \frac{2 + \sqrt{3}}{2 + \sqrt{3}}\)
\(= \frac{2 + \sqrt{3}}{2^2 - (\sqrt{3})^2} = \frac{2 + \sqrt{3}}{4 - 3} = \frac{2 + \sqrt{3}}{1}\)
Thus, the multiplicative inverse in simplest form = \(2 + \sqrt{3}\)
📦 Example 5
In the opposite figure: A covered glass aquarium in the shape of a rectangular prism for displaying fish, find:
- The volume of the glass aquarium.
- The total surface area of the aquarium to the nearest m².
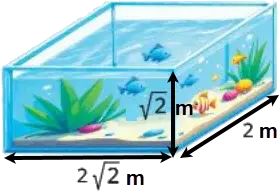
Solution:
1. Volume of the Glass Aquarium (V):
\(V = L \times W \times H\)
\(= 2\sqrt{2} \times 2 \times \sqrt{2}\)
\(= (2 \times 2) \times (\sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{2})\)
\(= 4 \times 2 = 8\) m³
✅ The volume of the aquarium is 8 m³.
2. Total Surface Area of the Aquarium (A) (nearest m²):
\(A = 2(LW + WH + LH)\)
\(= 2\bigl((2\sqrt{2} \times 2) + (2 \times \sqrt{2}) + (2\sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{2})\bigr)\)
\(= 2(4\sqrt{2} + 2\sqrt{2} + 4)\)
\(= 2(6\sqrt{2} + 4) = 12\sqrt{2} + 8\)
Approximate using \(\sqrt{2} \approx 1.414\):
\(A \approx 12 \times 1.414 + 8\)
\(\approx 16.968 + 8 = 24.968\)
Rounding to nearest m²: \(A \approx 25\) m²
✅ The total surface area of the aquarium is 25 m².
🌷 Example 6
In the figure, there is a flowerbed whose base is in the shape of a trapezoid. Find the area of the base of the flowerbed.
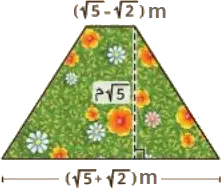
Solution:
The shape of the flowerbed's base is a trapezoid. The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:
\(A = \frac{1}{2} (b_1 + b_2) \times h\)
Where:
- \(b_1\) is the length of the first base (top base)
- \(b_2\) is the length of the second base (bottom base)
- \(h\) is the height
From the figure, we have:
- \(b_1 = (\sqrt{5} - \sqrt{2})\) m
- \(b_2 = (\sqrt{5} + \sqrt{2})\) m
- \(h = \sqrt{5}\) m
Now, substitute these values into the formula:
\(A = \frac{1}{2} \bigl[(\sqrt{5} - \sqrt{2}) + (\sqrt{5} + \sqrt{2})\bigr] \times \sqrt{5}\)
First, simplify inside the parentheses:
\(A = \frac{1}{2} (2\sqrt{5}) \times \sqrt{5}\)
Multiply \(\frac{1}{2}\) by \(2\sqrt{5}\):
\(A = \sqrt{5} \times \sqrt{5}\)
Since \(\sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{a} = a\):
\(A = 5\) m²
✅ Therefore, the area of the base of the flowerbed is 5 m².
